【系列文章】
重学ElasticSearch (ES) 系列(一):核心概念及安装
重学ElasticSearch (ES) 系列(二):搜索外相关操作(集群、索引、文档)
重学ElasticSearch (ES) 系列(四):ELK搭建SpringBoot日志实时分析系统
重学ElasticSearch (ES) 系列(五):常见面试题
目录
- 一、搜索相关性算分
- 二、搜索语法
- 2.1、查询表达式
- 2.1.1、match_all 查询所有文档
- 2.1.2、match 单个字段匹配
- 2.1.3、multi_match 多字段匹配
- 2.1.4、match_phrase 短语匹配
- 2.1.5、term 单值精确查询
- 2.1.6、terms 多值精确匹配
- 2.1.7、prefix 前缀匹配
- 2.1.8、wildcard 通配符匹配
- 2.1.9、regexp 正则匹配
- 2.1.10、fuzzy 近似匹配
- 2.1.11、range 区间匹配
- 2.1.12、exists 匹配指定字段非空的文档
- 2.1.13、ids id数值匹配
- 2.1.14、query_string 字符串匹配
- 2.2、复合条件搜索
- 2.2.1、bool 布尔查询(常用)
- 2.2.2、boosting query 提高查询
- 2.2.3、constant_score 固定分数查询
- 2.2.4、dis_max 最佳匹配查询
- 2.2.5、function_score 函数查询
- 2.3、其他筛选
- 三、搜索技巧记录
- 3.1、精确匹配
- 3.2、范围筛选
- 3.3、分词技巧
- 3.4、全匹配优先
- 3.5、Suggester API搜索提示
- 3.5.1、Term Suggester(纠错补全)
- 3.5.2、Phrase Suggester(补全短语)
- 3.5.3、Completion Suggester(自动补全)
- 3.5.4、Context Suggester(上下文提示)
- 3.6、实例:实现 and or嵌套查询
- 四、跨集群搜索
一、搜索相关性算分
【相关性算分】
一个文档与查询语句的匹配程度
【算分算法】
ES 5之前默认的算分采用TF-IDF,ES 5之后采用BM 25
1.1、TF-IDF
1.1.1、TF-IDF原理
TF-IDF = TF * IDF
【TF】
词频:词语在文本中出现的频率
【IDF】
逆向文件频率:log(全部文档数/检索词出现的文档数)
【例如】:搜索"区块链的应用"
1、会被分词为:“区块链”、“的”、“应用”
2、分别计算TF 和 IDF
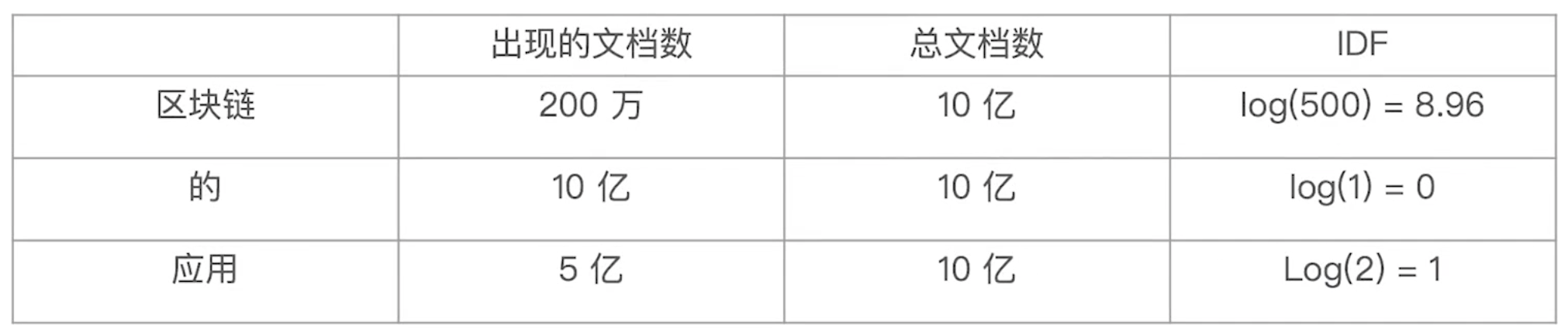
3、求和算分
Score = TF(区块链)*IDF(区块链) + TF(的)*IDF(的) + TF(应用)*IDF(应用)
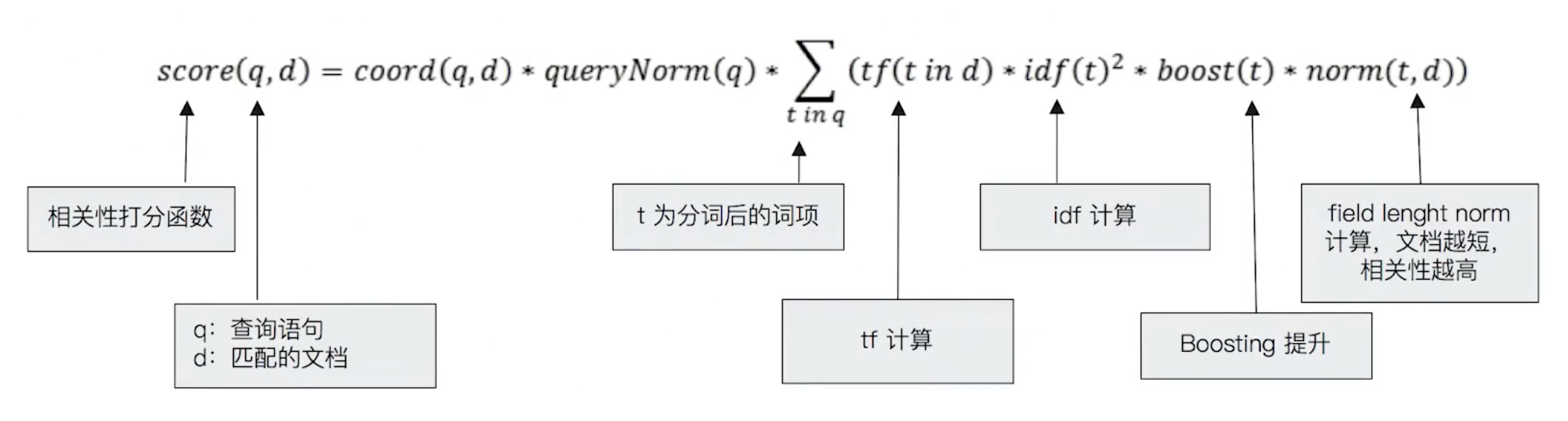
1.1.2、ES中对TF-IDF的应用
ES的TF-IDF算分公式:增加了Boosting提升,增加了field length norm来控制分数
1.2、BM 25
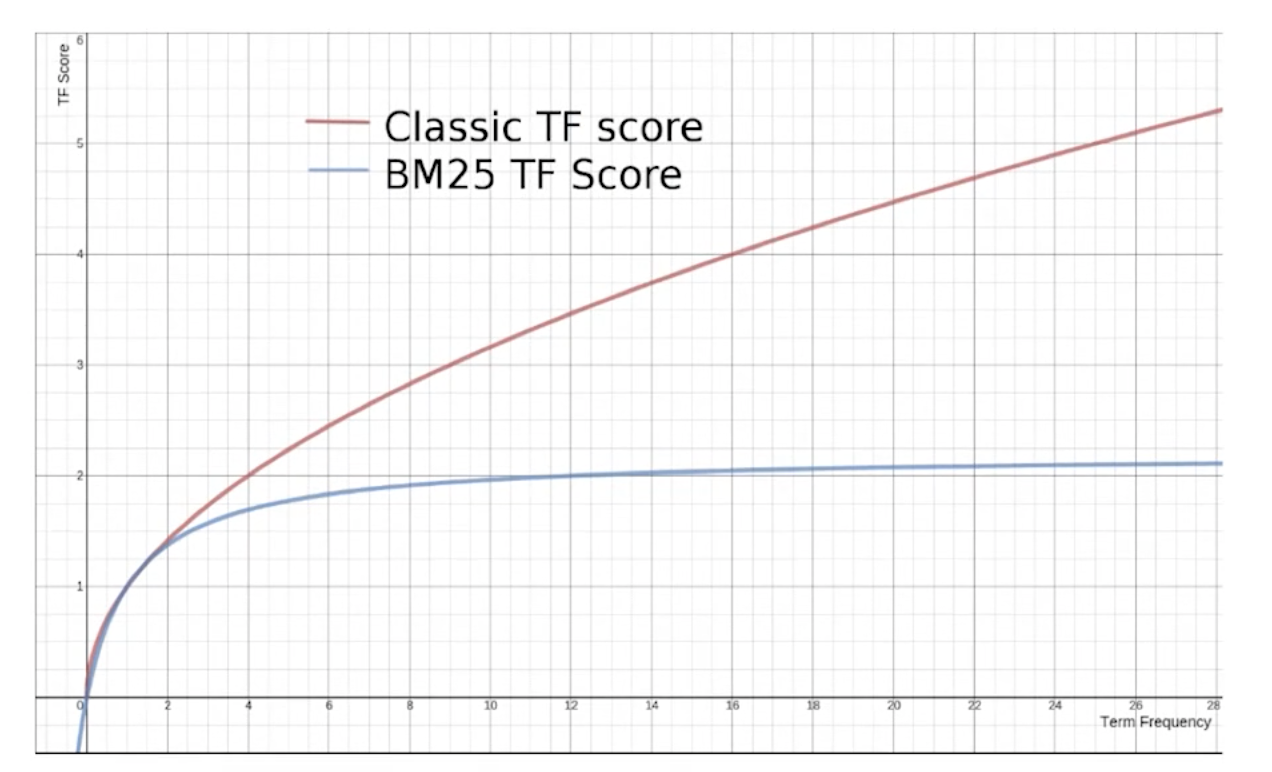
1.2.1、算法原理
BM 25是在TF-DF基础上做了一个收敛。
避免了TF无限增长时得分无限增长的问题

1.2.2、Explain API查看算分过程
搜索时添加explain参数,可以返回详细的算分过程
POST my_index/_search
{
"explain": true,
"query": {
"match": {"title": "数据"}
}
}
复制二、搜索语法
2.1、查询表达式
2.1.1、match_all 查询所有文档
查询所有文档
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
复制2.1.2、match 单个字段匹配
单个字段的查询
Keyword:不分词精确匹配
Text:分词后匹配
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "数据库", # text的会匹配"数据库"、"数据"...
"boost": 5 # boosting提升
}
}
}
复制2.1.3、multi_match 多字段匹配
多字段查询,支持^5设置boost
Keyword:不分词精确匹配
Text:分词匹配
Type:
(1)最佳字段(best_fields):取fields中分数最高的
(2)混合字段(cross_field):类似于copy_to,就是类似于把所有字段文字都拼接起来,然后算评分
-
best_fields
POST /my_index/_doc/_search { "query": { "multi_match": { "type": "best_fields", # 取fields中最高的评分 "query": "数据库", "fields": ["title^5","content"], # 支持^5设置boost "tie_breaker": 0.2, # 其他字段评分*0.2与最高求和,并做标准化处理 "minimum_should_match": "50%" # 搜索词分词后,50%的词要在title/content中 } } }复制 -
cross_fields
POST /my_index/_doc/_search { "query": { "multi_match": { "type": "cross_fields", # fields中字段全部拼接到一起算分 "operator": "and" "query": "数据库", "fields": ["title^5","content"], # 与copy_to相比,其优势是可以在搜索时为单个字段提升权重 } } }复制
2.1.4、match_phrase 短语匹配
短语匹配查询,slop表示分词的跨度,指分词和分词之间可以相隔多少个词,缺失了这些词仍然可以查到结果
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": {
"query": "数据库",
"slop": 4,
"boost": 5
}
}
}
}
复制2.1.5、term 单值精确查询
单个字段的精确查询
Keyword:不分词精确匹配
Text:不分词匹配
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"title": {
"value": "数据库", # text的会只会匹配"数据库"。
"boost": 5
}
}
}
}
复制2.1.6、terms 多值精确匹配
精确匹配多个值,只要被查字段包含指定数组中任何一个值就算符合条件
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"title": ["数据库", "java"],
"boost": 5
}
}
}
复制2.1.7、prefix 前缀匹配
匹配符合前缀要求的倒排索引数据。
注意:需要区分大小写,搜索词要是小写(或者定义mapping和settings的时候给这个字段设置忽略大小写),因为文档的词都是小写的
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"title": {
"value": "postgre", # 小写
"boost": 5
}
}
}
}
复制2.1.8、wildcard 通配符匹配
通配符(*表示任何字符串,?表示任何单个字符)匹配倒排索引
注意:需要区分大小写,搜索词要是小写(或者定义mapping和settings的时候给这个字段设置忽略大小写),因为文档的词都是小写的
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"title": {
"value": "*gresql", # 小写
"boost": 5
}
}
}
}
复制2.1.9、regexp 正则匹配
正则表达式匹配倒排索引
注意:需要区分大小写,搜索词要是小写(或者定义mapping和settings的时候给这个字段设置忽略大小写),因为文档的词都是小写的
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"title": {
"value": ".*gresql", # 小写
"boost": 5
}
}
}
}
复制2.1.10、fuzzy 近似匹配
fuzziness用于控制levenshtein距离
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"fuzzy": {
"title": {
"value": "postgre", # 小写
"fuzziness": 4, # 容错字符数,比如aostgre容错4的话,可以匹配到postgresql
"boost": 5
}
}
}
}
复制2.1.11、range 区间匹配
区间匹配,
可以使用:gt(大于)、gte(大于等于)、lt(小于)、lte(小于等于)
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"count": {
"gte": 200,
"lt": 250
}
}
}
}
复制2.1.12、exists 匹配指定字段非空的文档
查询指定字段值不为null的数据,用于把某个字段不为null的文档往前排
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
# 给title不为null的文档boost*5
"exists": {
"field": "title",
"boost": 5
}
}
}
复制2.1.13、ids id数值匹配
用于通过文档id数组匹配文档
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": [1,3]
}
}
}
复制2.1.14、query_string 字符串匹配
字符串的专用匹配,可以多个条件、多个字段进行匹配
POST /my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
# 匹配title/content中,包含this且包含that的文档
"query_string": {
"fields": ["mysql", "oracle"],
"query": "mysql AND oracle",
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"boost": 5
}
}
}
复制2.2、复合条件搜索
复合查询有:
bool query(布尔查询)、boosting query(提高查询)、constant_score(固定分数查询)、dis_max(最佳匹配查询)、function_score(函数查询)。
2.2.1、bool 布尔查询(常用)
bool查询是一个或者多个查询子句的组合,支持must 、must not、should、filter四种子句。
-
复合查询嵌套语法
【Query Context 】
must :必须匹配,参与算分
should :选择性匹配、参与算分
【Filter Context 】
must not:必须不匹配,不参与算分
filter:必须匹配,不参与算分, 可以使用缓存
POST knowledge/_doc/_search { "query": { # 1、bool子查询可以任意顺序出现 # 2、可以同时多个子查询 "bool": { "filter": { "term": {"isIndex": "true"} }, "must_not": { "range": { "price": {"lte": 30} } }, # 3、子查询也能是数组(多个查询) "should": [ {"match": {"title": {"query": "文章"}}}, {"match": {"content": {"query": "文章"}}} ], "must": [ {"term": {"price": 60}}, # 4、子查询也能嵌套bool { "bool": { "should": [ {"term": {"role": "teacher"}}, {"term": {"role": "student"}} ] } } ], # 5、如果没有must条件,should中必须有1个条件满足 "minimum_should_match": 1 } } }复制 -
嵌套查询算分
1、每个参与算分的子句计算的评分会被合并到总的评分中。
2、查询语句的结构,会对相关度算分产生影响
(1)不指定boost时,同一级的子句,具有相同权重,得分相加
(2)可以通过boost提升权重:boost>1增加权重;0-1降低权重;boost<0负分
POST knowledge/_doc/_search { "query": { "bool": { "should": [ { "match": { "title": { "query": "文章", # boost提升权重 "boost": 4 } } }, { "match": { "content": { "query": "文章", "boost": 1 } } } ], "minimum_should_match": 1 } } }复制
2.2.2、boosting query 提高查询
当我们想把符合某个标准的放在后面,可以使用boosting query
如下:查询满足
positive的内容,并将满足negative的分数调低(score = score*negative_boost)
{
"query": {
# 查询带apple的内容
"boosting": {
"positive": {
"match": {
"content": "apple"
}
},
# 把带pie的特殊处理
"negative": {
"match": {
"content": "pie"
}
},
# 调小权重,放后面 (negative_boost参数一般小于1.0)
"negative_boost": 0.5
}
}
}
复制2.2.3、constant_score 固定分数查询
内部包装了过滤查询,故而不会计算相似度分,该查询返回的相似度分与字段上指定boost参数值相同
| 序号 | 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | filter | 必须,查询对象,指定希望执行的过滤查询,任何返回的文档都必须匹配这个查询;过滤查询不会计算相似度分,为提升性能,ES会对使用频率高的过滤查询的结果进行缓存 |
| 2 | boost | 可选,浮点数,该值作为匹配了以上filter的文档的相似度分,默认为1.0 |
{
"query": {
# 这样查出来的,评分全是2.5
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"match": {
"content":"apple"
}
},
"boost": 2.5
}
}
}
复制2.2.4、dis_max 最佳匹配查询
普通复合查询,同级子句的算分是直接求和
若一个文档同时满足多个查询子句,则dis_max查询计算分数规则如下;
1)、取匹配项最高的那个分数;
2)、将匹配项的分数与tie_breaker值相乘;
3)、将相乘得到的分数与最高分相加;
| 序号 | 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | queries | 必须,数组对象,包含一个或多个查询子句,返回的文档必须匹配一个或多个查询条件,匹配的条件越多则分数越高 |
| 2 | tie_breaker | 可选,浮点值,参数介于0与1.0之间,用于增加匹配条件文档额外的分,默认为0.0 |
{
"size": 5,
"query": {
"dis_max": {
"tie_breaker": 0.7,
"queries": [
{
"term": {
"city.keyword": {
"boost": 2,
"value": "Brogan"
}
}
},
{
"term": {
"gender.keyword": {
"boost": 1.0,
"value": "M"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
复制2.2.5、function_score 函数查询
用于在查询结束后,对每一个匹配的文档进行一系列的重新算分,根据新生成的分数进行排序
提供了几种默认的算分的函数
- Weight:对每份文档适用一个简单的提升,且该提升不会被归约:当weight为2时,结果为2 * _score。
- Field Value Factor:使用文档中某个字段的值来改变_score,比如将受欢迎程度或者投票数量考虑在内。
- Random Score:使用一致性随机分值计算来对每个用户采用不同的结果排序方式,对相同用户仍然使用相同的排序方式。
- 衰减函数:将像publish_date,geo_location或者price这类浮动值考虑到_score中,偏好最近发布的文档,邻近于某个地理位置(译注:其中的某个字段)的文档或者价格
- Script Score:使用自定义的脚本来完全控制分值计算逻辑。如果你需要以上预定义函数之外的功能,可以根据需要通过脚本进行实现。
提供了Boost Mode 和 Max Boost控制算分
【Boost Mode】
- Multiply:算分与函数值的乘积
- Sum:算分与函数的和
- Min/Max:算分与函数取 最小/最大值
- Replace:使用函数取代算分
【Max Boost】
将算分控制在一个最大值
-
一个Field Value Factor的例子
【modifier参数】
1、当没有modifier参数时:新的算分 = 老的算分 * 投票数。(这种当投票数很大或为0时,对结果影响太大了,可以使用modifier参数对投票数做收敛)
2、当modifier=log1p:新的算分 = 老的算分 * log(1 + 投票数)

【factor参数】
可以对收敛做更好的控制
新的算分 = 老的算分 * log(1 + factor*投票数)
{ "query": { "function_score": { "query": { "multi_match": { "query": "数据", "fields": ["title", "content"] } }, # 依据投票数调整算分 "field_value_factor": { "field": "votes", # Modifier平滑曲线 "modifier": "log1p", "factor": 0.1 }, # 得分相加:新的算分 = 老的算分 + log(1 + factor*投票数) "boost_mode": "sum", # 最大得分控制在3 "max_boost": 3 } } }复制 -
一个Random Score的例子
【使用场景】
网站的广告需要提高展现率
【具体需求】
让每个用户看到不同的排名,但是同一个用户访问时,顺序保持一致
{ "query": { "function_score": { # 随机排序 "random_score": { # seed不变,排序不变 "seed": 9999 } } } }复制
2.3、其他筛选
2.3.1、分页
需要注意的是,java的pagehelper分页起始是1,es的起止是0,所以,当想取第一页,传的是1时,记得-1
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"track_total_hits": true, # 设置返回数据具体总条数
"query": {}
}
复制2.3.2、返回数据具体总条数
track_total_hits参数默认为false
为false时,当搜索到的数据>10000条,则只显示10000条
为true时,可以显示详细条数
{
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"track_total_hits": true, # 设置返回数据具体总条数
"query": {}
}
复制2.3.3、高亮
给搜索匹配到的词高亮
-
高亮搜索
{ "query": {} # 高亮 "highlight" : { "pre_tags": ["<tag1>"], # 设置高亮标签,默认是<em></em> "post_tags": ["</tag2>"], "fields" : { "title" : {}, # 指定高亮的字段 "content": {} } } }复制 -
响应结果
{ "took" : 12, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 55065, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : 16.875015, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "knowledge", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "381945", "_score" : 16.875015, "_source" : { "title" : "数据库系统——数据库恢复技术" }, "highlight" : { "title" : [ "<tag1>数据</tag2><tag1>库</tag2>系统——<tag1>数据</tag2><tag1>库</tag2>恢复技术" ] } } ] } }复制
2.3.4、返回指定字段
不是所有字段都需要返回,可以指定需要返回的字段
可以使用通配符*
{
"from": 0,
"size": 1,
"query": {},
"_source": {
# 指定返回字段
"includes": [
"title"
],
# 指定不返回字段
"excludes": ["name","bir*"]
}
}
复制2.3.5、自定义排序
默认是根据score排序,可以指定自己的排序
排序需要用到正排索引,正排有两种:FieldData和DocValues。由于DocValues不支持对text的排序,所以,如果要对text类型的字段排序,需要开启FieldData
{
"query": {},
# 按照时间、score排序
"sort": [
{
"createdTime": {
"order": "desc"
}
},
{
"_score": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
复制三、搜索技巧记录
3.1、精确匹配
3.1.1、忽略大小写
text的创建文档时是会分词并且转成小写的,但是精确匹配keyword是不分词的,也不会转成小写。有时候我们想要忽略大小写的精确匹配,该如何做呢?
需要在创建索引的时候,设置忽略大小写
{
"settings": {
"number_of_replicas": 1,
"number_of_shards": 5,
# 1、指定忽略大小写
"analysis": {
"normalizer": {
"lowercase_normalizer": {
"type": "custom",
"char_filter": [],
"filter": [
"lowercase"
]
}
}
}
},
"mappings": {
"tag": {
"type": "keyword",
# 2、设置忽略大小写
"normalizer": "lowercase_normalizer"
}
}
}
复制3.1.2、数组元素
当我们一个数组的字段,需要创建文档,并且需要能搜索到时,我们改如何处理?
1、设置索引时,设置为keyword类型,并且可以设定忽略大小写匹配
2、创建文档的时候,存入数组类型
3、搜索时常规搜索即可
-
设置索引
{ "settings": { "number_of_replicas": 1, "number_of_shards": 5, # 1、指定忽略大小写 "analysis": { "normalizer": { "lowercase_normalizer": { "type": "custom", "char_filter": [], "filter": [ "lowercase" ] } } } }, "mappings": { "tags": { # 2、keyword "type": "keyword", # 3、设置忽略大小写 "normalizer": "lowercase_normalizer" } } }复制 -
创建文档
POST mapping_test/_doc/1 { "tags": ["mysql", "Oracle"] }复制 -
搜索
POST mapping_test/_search { "query": { "match": { # 这样搜索,就可以搜索到上面创建的文档 "tags": "oracle" } } }复制
3.2、范围筛选
范围查询符号
| 符号 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| gte | greater-than or equal to, 大于或等于 |
| gt | greater-than, 大于 |
| lte | less-than or equal to, 小于或等于 |
| lt | less-than, 小于 |
3.2.1、数值
数值存储为数值类型,可以进行范围查询
# 查询商品中40 <= price <= 80的文档
GET mapping_test/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"price": {
"gte": 40,
"lte": 80,
"boost": 2.0
}
}
}
}
复制3.2.2、时间
关于时间,也可以做范围查询
【时间数学表达式】
now:当前时间
now+1h—— 加1小时;now-1d—— 减1天;now/d—— 四舍五入到最近的一天.
表达式 含义 表达式 含义 y年 M月 w星期 d天 h小时 H小时 m分钟 s秒
-
创建索引
{ "mappings": { "createdTime": { # 时间格式 "type": "date", # 定义时间存储格式 "format": "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss" } } }复制 -
存入文档
{ "createdTime": "2022-01-03 22:13:14" }复制 -
时间筛选
# 近4个月 { "query": { "range": { "createdTime": { "gte": "now-4M", "format": "yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss" } } } } # [1950-01-11, 1990-01-11) { "query": { "range": { "createdTime": { "from": "1950-01-11", "to": "1990-01-11", "include_lower": true, "include_upper": false } } } }复制
3.3、分词技巧
索引时用ik_max_word(细粒度分词),在搜索时用ik_smart(粗粒度分词)
即:索引时最大化的将文章内容分词,搜索时更精确的搜索到想要的结果。
-
创建索引事时指定ik_max_word
{ "mappings": { "properties": { "content": { "type": "text", "analyzer": "ik_max_word", "fields": { "keyword": { "type": "keyword", "ignore_above": 256 } } } } }复制 -
搜索时使用ik_smart
{ "query": { "match": { "title": { "analyzer": "ik_smart", "query": "文章" } } } }复制
3.4、全匹配优先
【问题】
在真实场景中,我搜索"国产数据库排行",会被分词为"国产"、“数据库”、“排行"然后去文档中搜索,如果一个文档中不包含"国产"但是有很多"数据库”、“排行”,那这个文档会被排在前面,但是这并不是我们想要的,我们的关键点在"国产",那我们该如何做呢?
【解决方案】
在es里,提供了两个参数:
1、minimum_should_match:可以设置匹配度,比如设置为100%,那么就只会匹配到必须全包含"国产"、“数据库”、排行"的文档
2、boost:可以设置该项权重。因为我们如果只用minimum_should_match=100%匹配的话,得到的数据量太小少了,还应该包含一些与此相关的,比如有些叫"国产数据库排名"。那么我们就可以使用bool复合查询,把minimum_should_match=100%匹配的当做其中一个算分项,并且调大boost参数,让其往前排
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"title": {
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"query": "文章",
"minimum_should_match": "100%",
"boost": 20
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"title": {
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"query": "文章",
"boost": 2
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
复制3.5、Suggester API搜索提示
ES提供了suggseter api,提供了4种类型的suggseters:Term 、Phrase Suggester、Complete、Context Suggseter
【原理】
将输入的文本分解为Token,然后在索引的字段里查找相似的term返回
3.5.1、Term Suggester(纠错补全)
【场景】
当我们搜索postgresql的时候,不小心输成了postgrasql,给用户一个postgresql的提示
【实现方法】
搜索的时候,使用Term Suggester即可
【参数】
text建议文字。建议文本是必需的选项,需要全局或按建议设置。 field从中获取候选建议的字段。这是一个必需的选项,需要全局设置或根据建议设置。 analyzer用于分析建议文本的分析器。默认为建议字段的搜索分析器。 size每个建议文本标记返回的最大更正。 sort定义如何根据建议文本术语对建议进行排序。两个可能的值: score:先按分数排序,然后按文档频率排序,再按术语本身排序。frequency:首先按文档频率排序,然后按相似性分数排序,然后按术语本身排序。suggest_mode建议模式控制包含哪些建议或控制建议的文本术语,建议。可以指定三个可能的值: missing:仅提供不在索引词典中,但是在原文档中的词。这是默认值。popular:仅提供在索引词典中出现的词语。always:索引词典中出没出现的词语都要给出建议。
-
搜索
{ "query" : { "match": { "title": { "query": "posgresql" } } }, # 可以同时纠错猜多个词 "suggest": { "my-term-suggestion": { "text": "posgresql", "term": { "suggest_mode": "missing", "field": "title" } }, "my-term-suggestion2": { "text": "oracla", "term": { "suggest_mode": "missing", "field": "title" } } } }复制 -
返回
{ "took" : 5, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { }, "suggest" : { "my-term-suggestion" : [ { "text" : "posresql", "offset" : 0, "length" : 8, "options" : [ { "text" : "postgresql", "score" : 0.9, "freq" : 5426 }, { "text" : "postgresql-", "score" : 0.8, "freq" : 11 } ] } ], "my-term-suggestion2" : [ { "text" : "oracla", "offset" : 0, "length" : 6, "options" : [ { "text" : "oracle", "score" : 0.8333333, "freq" : 13835 } ] } }复制
3.5.2、Phrase Suggester(补全短语)
【场景】
跟Term Suggester一样,也是做词的纠错的。在term的基础上,会考量多个term之间的关系,比如是否同时出现在索引的原文里,相邻程度,以及词频等
【实现方法】
搜索的时候,使用Term Suggester即可
-
搜索
{ "suggest" : { "my-phrase-suggest":{ "text": "posgaresql", "phrase": { "field": "title" } } } }复制 -
结果
{ "took" : 4, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 0, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : null, "hits" : [ ] }, "suggest" : { "my-phrase-suggest" : [ { "text" : "posgaresql", "offset" : 0, "length" : 10, "options" : [ { "text" : "postgresql ar sql", "score" : 1.463355E-4 }, { "text" : "posgresql ar sql", "score" : 7.268909E-6 }, { "text" : "posrgresql ar sql", "score" : 4.6641644E-6 } ] } ] } }复制
3.5.3、Completion Suggester(自动补全)
【场景】
用户每输入一个字符,就需要即时发送一个查询请求查找匹配项。比如你输入"postgr",就会提示出"postgresql数据库排行榜位居第一"
【原理】
由于这个是实时的,对性能要求比较高,所以采用了非倒排索引的方式来完成。将数据编码成FST和索引一起存放,FST会被整个加载到内存中,所以速度很快。
但是FST只能用于前缀查找
【实现方法】
1、需要在创建索引的时候在mapping里面设置
2、在存储文档的时候,需要往该字段中存数据
3、使用my_index/_search?pretty来调用api
-
创建索引
PUT mapping_test { "mappings": { "properties": { "title_completion": { "type": "completion" }, "title": { "type": "text" } } } }复制 -
创建文档
POST mapping_test/_doc/1 { "title_completion": "postgresql oracle 苹果", "title": "postgresql oracle 苹果" }复制 -
API调用
POST mapping_test/_search?pretty { "suggest": { "my-title-completion": { "prefix": "oracle", "completion": { "field": "title_completion" } } } }复制 -
返回结果
{ "took" : 1, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 0, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : null, "hits" : [ ] }, "suggest" : { "my-title-completion" : [ { "text" : "oracle", "offset" : 0, "length" : 6, "options" : [ ] } ] } }复制
3.5.4、Context Suggester(上下文提示)
【场景】
当用户输入"star",当与咖啡相关的时,提示"starbucks";当电影相关时,提示"star wars"
【实现方法】
1、需要在创建索引的时候在mapping里面设置
2、在存储文档的时候,需要往该字段中存数据
3、使用my_index/_search?pretty来调用api
-
创建索引
PUT mapping_test { "mappings": { "properties": { "title_completion": { "type": "completion", "contexts": [{ "type": "category", "name": "my_title_category" }] }, "title": { "type": "text" } } } }复制 -
创建文档
POST mapping_test/_doc/1 { "title_completion": { "input": ["star war"], "contexts": { "my_title_category": "movies" } }, "title": "I love the star war movies" } POST mapping_test/_doc/2 { "title_completion": { "input": ["starbucks"], "contexts": { "my_title_category": "coffee" } }, "title": "Where can I find a Starbucks" }复制 -
搜索
POST mapping_test/_search { "suggest": { "my-title-completion": { "prefix": "sta", "completion": { "field": "title_completion", "contexts": { "my_title_category": "coffee" } } } } }复制 -
搜索结果
{ "took" : 663, "timed_out" : false, "_shards" : { "total" : 1, "successful" : 1, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : { "value" : 0, "relation" : "eq" }, "max_score" : null, "hits" : [ ] }, "suggest" : { "my-title-completion" : [ { "text" : "sta", "offset" : 0, "length" : 3, "options" : [ { "text" : "starbucks", "_index" : "mapping_test", "_type" : "_doc", "_id" : "2", "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "title_completion" : { "input" : [ "starbucks" ], "contexts" : { "my_title_category" : "coffee" } }, "title" : "Where can I find a Starbucks" }, "contexts" : { "my_title_category" : [ "coffee" ] } } ] } ] } }复制
3.6、实例:实现 and or嵌套查询
如何实现类似sql的where条件灵活筛选呢?比如
where (条件1 and (条件2 or 条件3)) or (条件4 and 条件5)复制【心得】
1、多条件就嵌套bool,and就must 、or就should
2、划分:整体划分为bool-should: (条件1 and (条件2 or 条件3))、(条件4 and 条件5)。往下拆分
(1)bool-must: 条件1 、 (条件2 or 条件3)
(1.1)bool-should: 条件2、条件3
(2)bool-must: 条件4、条件5
POST my_index/_doc/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"minimum_should_match": 1,
// (条件1 and (条件2 or 条件3)) or (条件4 and (条件5 or 条件6))
"should": [
// (条件1 and (条件2 or 条件3))
{
"bool": {
"must": [
// 条件1
{
"term": {
"name": "名字"
}
},
// (条件2 or 条件3)
{
"bool": {
"should": [
// 条件2
{
"term": {
"age": 13
}
},
// 条件3
{
"term": {
"age": 15
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
},
// (条件4 and 条件5)
{
"bool": {
"must": [
// 条件4
{
"term": {
"age": 16
}
},
// 条件5
{
"term": {
"age": 17
}
}
]
}
}
]
}
}
}
复制四、跨集群搜索
由于es支持集群的水平扩展,所以跨集群的搜索是很有必要的
ES 5.3引入了跨集群搜索的功能
【如何使用】
1、对每个集群做设置
2、跨集群搜索
-
本地启动三个集群用于测试
bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node1 -E cluster.name=cluster_name path.data=node1_data -d -E discovery.type=single-node -E http.port=9200 -E transport.port=9300 bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node2 -E cluster.name=cluster_name path.data=node2_data -d -E discovery.type=single-node -E http.port=9201 -E transport.port=9301 bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node3 -E cluster.name=cluster_name path.data=node3_data -d -E discovery.type=single-node -E http.port=9202 -E transport.port=9302复制 -
对每个集群做设置
每个集群里都要执行一遍该命令
PUT _cluster/settings { "presistent": { "cluster": { "remote": { "cluster_one": { "seeds": [ "127.0.0.1:9200" ] }, "cluster_two": { "seeds": [ "127.0.0.1:9201" ] }, "cluster_three": { "seeds": [ "127.0.0.1:9202" ] } } } } }复制 -
各个集群分别创建文档
POST users/_doc/1 {"name": "user1", "age": 11} POST mapping_test/_doc/1 {"name": "user2", "age": 12} POST mapping_test/_doc/1 {"name": "user3", "age": 13}复制 -
跨集群搜索
GET /users,cluster1:users,cluster2:users,cluster3:users/_search { "query": { "match_all": {} } }复制
评论
 点赞
点赞






