前言:上篇文章HBase Filter 过滤器概述对HBase过滤器的组成及其家谱进行简单介绍,本篇文章主要对HBase过滤器之比较器作一个补充介绍,也算是HBase Filter学习的必备低阶魂技吧。本篇文中源码基于HBase 1.1.2.2.6.5.0-292 HDP版本。

HBase所有的比较器实现类都继承于父类ByteArrayComparable,而父类 ByteArrayComparable 又实现了 Comparable 接口;不同功能的比较器差别在于对父类 compareTo() 方法的重写逻辑不同。
Hbase Comparator家谱如下:
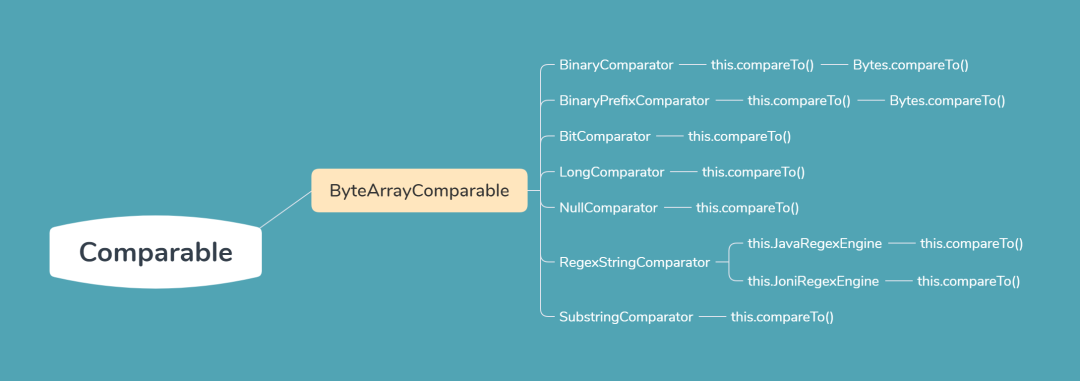
下面分别对HBase Filter默认实现的七大比较器一一进行介绍。
1. BinaryComparator
介绍:二进制比较器,用于按字典顺序比较指定字节数组。
先看一个小例子:
1public class BinaryComparatorDemo {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4
5 BinaryComparator bc = new BinaryComparator(Bytes.toBytes("bbb"));
6
7 int code1 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("bbb"), 0, 3);
8 System.out.println(code1); // 0
9 int code2 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("aaa"), 0, 3);
10 System.out.println(code2); // 1
11 int code3 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("ccc"), 0, 3);
12 System.out.println(code3); // -1
13 int code4 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("bbf"), 0, 3);
14 System.out.println(code4); // -4
15 int code5 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("bbbedf"), 0, 6);
16 System.out.println(code5); // -3
17 }
18}复制
不难看出,该比较器的比较规则如下:
两个字符串首字母不同,则该方法返回首字母的asc码的差值
参与比较的两个字符串如果首字符相同,则比较下一个字符,直到有不同的为止,返回该不同的字符的asc码差值
两个字符串不一样长,可以参与比较的字符又完全一样,则返回两个字符串的长度差值
看一下以上规则对应其compareTo()方法的源码实现。
实现一:
1static enum UnsafeComparer implements Bytes.Comparer<byte[]> {
2INSTANCE;
3....
4public int compareTo(byte[] buffer1, int offset1, int length1, byte[] buffer2, int offset2, int length2) {
5 if (buffer1 == buffer2 && offset1 == offset2 && length1 == length2) {
6 return 0;
7 } else {
8 int minLength = Math.min(length1, length2);
9 int minWords = minLength / 8;
10 long offset1Adj = (long)(offset1 + BYTE_ARRAY_BASE_OFFSET);
11 long offset2Adj = (long)(offset2 + BYTE_ARRAY_BASE_OFFSET);
12 int j = minWords << 3;
13
14 int offset;
15 for(offset = 0; offset < j; offset += 8) {
16 long lw = theUnsafe.getLong(buffer1, offset1Adj + (long)offset);
17 long rw = theUnsafe.getLong(buffer2, offset2Adj + (long)offset);
18 long diff = lw ^ rw;
19 if (diff != 0L) {
20 return lessThanUnsignedLong(lw, rw) ? -1 : 1;
21 }
22 }
23
24 offset = j;
25 int b;
26 int a;
27 if (minLength - j >= 4) {
28 a = theUnsafe.getInt(buffer1, offset1Adj + (long)j);
29 b = theUnsafe.getInt(buffer2, offset2Adj + (long)j);
30 if (a != b) {
31 return lessThanUnsignedInt(a, b) ? -1 : 1;
32 }
33
34 offset = j + 4;
35 }
36
37 if (minLength - offset >= 2) {
38 short sl = theUnsafe.getShort(buffer1, offset1Adj + (long)offset);
39 short sr = theUnsafe.getShort(buffer2, offset2Adj + (long)offset);
40 if (sl != sr) {
41 return lessThanUnsignedShort(sl, sr) ? -1 : 1;
42 }
43
44 offset += 2;
45 }
46
47 if (minLength - offset == 1) {
48 a = buffer1[offset1 + offset] & 255;
49 b = buffer2[offset2 + offset] & 255;
50 if (a != b) {
51 return a - b;
52 }
53 }
54
55 return length1 - length2;
56 }
57}复制
实现二:
1static enum PureJavaComparer implements Bytes.Comparer<byte[]> {
2 INSTANCE;
3
4 private PureJavaComparer() {
5 }
6
7 public int compareTo(byte[] buffer1, int offset1, int length1, byte[] buffer2, int offset2, int length2) {
8 if (buffer1 == buffer2 && offset1 == offset2 && length1 == length2) {
9 return 0;
10 } else {
11 int end1 = offset1 + length1;
12 int end2 = offset2 + length2;
13 int i = offset1;
14
15 for(int j = offset2; i < end1 && j < end2; ++j) {
16 int a = buffer1[i] & 255;
17 int b = buffer2[j] & 255;
18 if (a != b) {
19 return a - b;
20 }
21
22 ++i;
23 }
24
25 return length1 - length2;
26 }
27 }
28}复制
实现一是对实现二的一个优化,都引自Bytes类,但实现一是不安全的,HBase优先执行实现一方案,如果有异常再执行实现二方案。如下:
1public static int compareTo(byte[] buffer1, int offset1, int length1, byte[] buffer2, int offset2, int length2) {
2 return Bytes.LexicographicalComparerHolder.BEST_COMPARER.compareTo(buffer1, offset1, length1, buffer2, offset2, length2);
3}
4...
5...
6
7static final String UNSAFE_COMPARER_NAME = Bytes.LexicographicalComparerHolder.class.getName() + "$UnsafeComparer";
8static final Bytes.Comparer<byte[]> BEST_COMPARER = getBestComparer();
9static Bytes.Comparer<byte[]> getBestComparer() {
10 try {
11 Class<?> theClass = Class.forName(UNSAFE_COMPARER_NAME);
12 Bytes.Comparer<byte[]> comparer = (Bytes.Comparer)theClass.getEnumConstants()[0];
13 return comparer;
14 } catch (Throwable var2) {
15 return Bytes.lexicographicalComparerJavaImpl();
16 }
17}复制
该比较器compareTo()方法实现算是这些比较器中最复杂的一个,相关代码可以借鉴复用。
2. BinaryPrefixComparator
介绍:二进制比较器,只比较前缀是否与指定字节数组相同。
先看一个小例子:
1public class BinaryPrefixComparatorDemo {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4
5 BinaryPrefixComparator bc = new BinaryPrefixComparator(Bytes.toBytes("b"));
6
7 int code1 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("bbb"), 0, 3);
8 System.out.println(code1); // 0
9 int code2 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("aaa"), 0, 3);
10 System.out.println(code2); // 1
11 int code3 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("ccc"), 0, 3);
12 System.out.println(code3); // -1
13 int code4 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("bbf"), 0, 3);
14 System.out.println(code4); // 0
15 int code5 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("bbbedf"), 0, 6);
16 System.out.println(code5); // 0
17 int code6 = bc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("ebbedf"), 0, 6);
18 System.out.println(code6); // -3
19 }
20}复制
该比较器只是基于BinaryComparator比较器稍作更改而已,以下代码一目了然:
1public int compareTo(byte[] value, int offset, int length) {
2 return Bytes.compareTo(this.value, 0, this.value.length, value, offset, this.value.length <= length ? this.value.length : length);
3}复制
看一下同BinaryComparator方法的异同:
1public int compareTo(byte[] value, int offset, int length) {
2 return Bytes.compareTo(this.value, 0, this.value.length, value, offset, length);
3}复制
区别只在于最后一个传参,即length=min(this.value.length,value.length),取小。这样在后面的字节逐位比较时,即只需比较min length次。
3. BitComparator
介绍:位比价器,通过BitwiseOp提供的AND(与)、OR(或)、NOT(非)进行比较。返回结果要么为1要么为0,仅支持 EQUAL 和非 EQUAL。
先看一个小例子:
1public class BitComparatorDemo {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4
5 // 长度相同按位或比较:由低位起逐位比较,每一位按位或比较都为0,则返回1,否则返回0。
6 BitComparator bc1 = new BitComparator(new byte[]{0,0,0,0}, BitComparator.BitwiseOp.OR);
7 int i = bc1.compareTo(new byte[]{0,0,0,0}, 0, 4);
8 System.out.println(i); // 1
9 // 长度相同按位与比较:由低位起逐位比较,每一位按位与比较都为0,则返回1,否则返回0。
10 BitComparator bc2 = new BitComparator(new byte[]{1,0,1,0}, BitComparator.BitwiseOp.AND);
11 int j = bc2.compareTo(new byte[]{0,1,0,1}, 0, 4);
12 System.out.println(j); // 1
13 // 长度相同按位异或比较:由低位起逐位比较,每一位按位异或比较都为0,则返回1,否则返回0。
14 BitComparator bc3 = new BitComparator(new byte[]{1,0,1,0}, BitComparator.BitwiseOp.XOR);
15 int x = bc3.compareTo(new byte[]{1,0,1,0}, 0, 4);
16 System.out.println(x); // 1
17 // 长度不同,返回1,否则按位比较
18 BitComparator bc4 = new BitComparator(new byte[]{1,0,1,0}, BitComparator.BitwiseOp.XOR);
19 int y = bc4.compareTo(new byte[]{1,0,1}, 0, 3);
20 System.out.println(y); // 1
21 }
22}复制
上述注释阐述的规则,对应以下代码:
1public int compareTo(byte[] value, int offset, int length) {
2 if (length != this.value.length) {
3 return 1;
4 } else {
5 int b = 0;
6
7 for(int i = length - 1; i >= 0 && b == 0; --i) {
8 switch(this.bitOperator) {
9 case AND:
10 b = this.value[i] & value[i + offset] & 255;
11 break;
12 case OR:
13 b = (this.value[i] | value[i + offset]) & 255;
14 break;
15 case XOR:
16 b = (this.value[i] ^ value[i + offset]) & 255;
17 }
18 }
19
20 return b == 0 ? 1 : 0;
21 }
22}复制
核心思想就是:由低位起逐位比较,直到b!=0退出循环。
4. LongComparator
介绍:Long 型专用比较器,返回值:0 -1 1。上篇概述没有提到,这里补上。
先看一个小例子:
1public class LongComparatorDemo {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 LongComparator longComparator = new LongComparator(1000L);
5 int i = longComparator.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes(1000L), 0, 8);
6 System.out.println(i); // 0
7 int i2 = longComparator.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes(1001L), 0, 8);
8 System.out.println(i2); // -1
9 int i3 = longComparator.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes(998L), 0, 8);
10 System.out.println(i3); // 1
11 }
12}复制
这个比较器实现相当简单,不多说了,如下:
1public int compareTo(byte[] value, int offset, int length) {
2 Long that = Bytes.toLong(value, offset, length);
3 return this.longValue.compareTo(that);
4}复制
可以看到,实现一个简单的比较器并不是那么麻烦。
5. NullComparatorDemo
介绍:控制比较式,判断当前值是不是为null。是null返回0,不是null返回1,仅支持 EQUAL 和非 EQUAL。
先看一个小例子:
1public class NullComparatorDemo {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 NullComparator nc = new NullComparator();
5 int i1 = nc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("abc"));
6 int i2 = nc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes(""));
7 int i3 = nc.compareTo(null);
8 System.out.println(i1); // 1
9 System.out.println(i2); // 1
10 System.out.println(i3); // 0
11 }
12}复制
这个比较器实现相当简单,不多说了,如下:
1public int compareTo(byte[] value) {
2 return value != null ? 1 : 0;
3}复制
6. RegexStringComparator
介绍:提供一个正则的比较器,支持正则表达式的值比较,仅支持 EQUAL 和非 EQUAL。匹配成功返回0,匹配失败返回1。
先看一个小例子:
1public class RegexStringComparatorDemo {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 RegexStringComparator rsc = new RegexStringComparator("abc");
5 int abc = rsc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("abcd"), 0, 3);
6 System.out.println(abc); // 0
7 int bcd = rsc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("bcd"), 0, 3);
8 System.out.println(bcd); // 1
9
10 String check = "^([a-z0-9A-Z]+[-|\\.]?)+[a-z0-9A-Z]@([a-z0-9A-Z]+(-[a-z0-9A-Z]+)?\\.)+[a-zA-Z]{2,}$";
11 RegexStringComparator rsc2 = new RegexStringComparator(check);
12 int code = rsc2.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("zpb@163.com"), 0, "zpb@163.com".length());
13 System.out.println(code); // 0
14 int code2 = rsc2.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes("zpb#163.com"), 0, "zpb#163.com".length());
15 System.out.println(code2); // 1
16 }
17}复制
其compareTo()方法有两种引擎实现,对应两套正则匹配规则,分别是JAVA版和JONI版(面向JRuby),默认实现引擎为RegexStringComparator.EngineType.JAVA。如下:
1public int compareTo(byte[] value, int offset, int length) {
2 return this.engine.compareTo(value, offset, length);
3}
4
5public static enum EngineType {
6 JAVA,
7 JONI;
8
9 private EngineType() {
10 }
11}复制
具体实现都很简单,都是调用正则语法匹配。以下是JAVA EngineType 实现:
1public int compareTo(byte[] value, int offset, int length) {
2 String tmp;
3 if (length < value.length / 2) {
4 tmp = new String(Arrays.copyOfRange(value, offset, offset + length), this.charset);
5 } else {
6 tmp = new String(value, offset, length, this.charset);
7 }
8
9 return this.pattern.matcher(tmp).find() ? 0 : 1;
10}复制
JONI EngineType 实现:
1public int compareTo(byte[] value, int offset, int length) {
2 Matcher m = this.pattern.matcher(value);
3 return m.search(offset, length, this.pattern.getOptions()) < 0 ? 1 : 0;
4}复制
都很容易理解,不多说了。
7. SubstringComparator
介绍:判断提供的子串是否出现在value中,并且不区分大小写。包含字串返回0,不包含返回1,仅支持 EQUAL 和非 EQUAL。
先看一个小例子:
1public class SubstringComparatorDemo {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 String value = "aslfjllkabcxxljsl";
5 SubstringComparator sc = new SubstringComparator("abc");
6 int i = sc.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes(value), 0, value.length());
7 System.out.println(i); // 0
8
9 SubstringComparator sc2 = new SubstringComparator("abd");
10 int i2 = sc2.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes(value), 0, value.length());
11 System.out.println(i2); // 1
12
13 SubstringComparator sc3 = new SubstringComparator("ABC");
14 int i3 = sc3.compareTo(Bytes.toBytes(value), 0, value.length());
15 System.out.println(i3); // 0
16 }
17}复制
这个比较器实现也相当简单,不多说了,如下:
1public int compareTo(byte[] value, int offset, int length) {
2 return Bytes.toString(value, offset, length).toLowerCase().contains(this.substr) ? 0 : 1;
3}复制
到此,七种比较器就介绍完了。如果对源码不敢兴趣,也建议一定要看看文中的小例子,熟悉下每种比较器的构造函数及结果输出。后续在使用HBase过滤器的过程中,会经常用到。当然除了这七种比较器,大家也可以自定义比较器。感谢关注老店,帮忙点个在看呗!
往期文章精选
HBase 官方社区推荐必读好文
HBase 原理|HBase 内存管理之 MemStore 进化论
HBase 实践|说好不哭,但 HBase 2.0 真的好用到哭
HBase 抗战总结|阿里巴巴 HBase 高可用8年抗战回忆录
关注 HBase 技术社区,获取更多技术干货







