作者
digoal
日期
2017-09-14
标签
PostgreSQL , 点面视觉输出 , subquery , nestloop join , 空间索引 , gist
背景
在新零售、快递等行业,有大量的点数据(例如包裹位置、快递员位置、仓库位置等),同时有大量的面数据(如小区,商圈,写字楼等)。
如何判断实时的正在配送的包裹落在哪个面呢?并且将之联系起来。
这个从视觉角度来思考,非常简单。
例如有一个地图,将其划分为若干个面(例如前面提到的小区)。
然后有一些小点,这些是POINT数据。
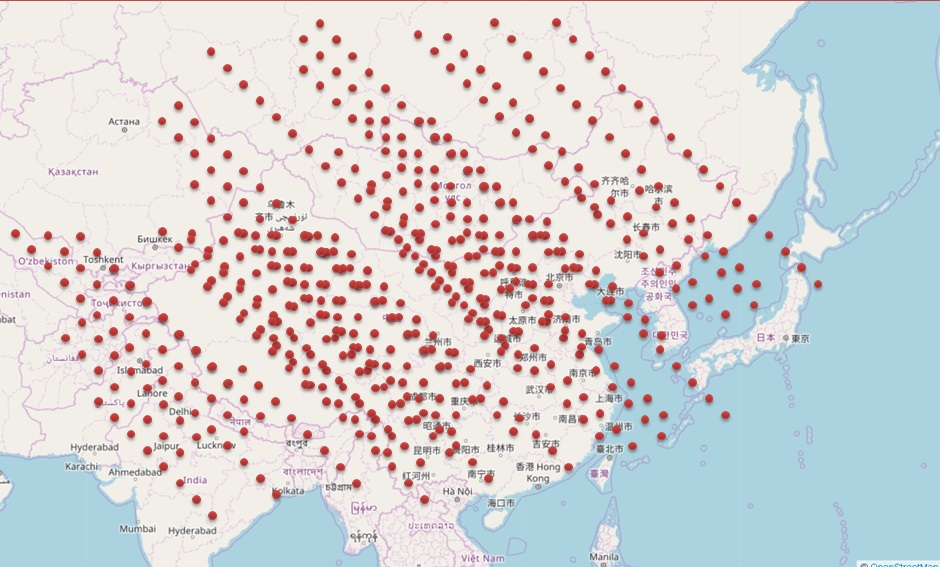
我们从图上一眼就能看出每个点落在哪个小区(面)里面。
在数据库中,这可能是两份数据(一份为点,一份为面)。输出的实际上是点+面(ID)的数据。
怎么做到高效的输出呢?
DEMO
搜索某些订单,当前处于哪个面。这是非常典型的点面判断需求。
接下来的例子,有25万个面,查询若干笔订单属于哪个面。
1、创建、生成静态的面数据(通常面的数据是静态的,例如小区,商圈,大楼,仓库覆盖范围等)
```
postgres=# create table t2(id int, pos box);
CREATE TABLE
-- 在(0,0)到(500,500)的平面上,划分成251001个正方形的小面。
postgres=# do language plpgsql $$
declare
x int;
y int;
begin
for x in 0..500 loop
for y in 0..500 loop
insert into t2 values (x+y, box(point(x,y),point(x+1,y+1)));
end loop;
end loop;
end;
$$;
DO
postgres=# select count(*) from t2;
count
251001
(1 row)
```
创建空间索引
postgres=# create index idx_t2 on t2 using gist(pos);
CREATE INDEX
2、创建、生成点的数据。
postgres=# create table t1(id int, pos point);
CREATE TABLE
```
-- 在(0,0),(500,500)的平面上,生成10000个随机的点
postgres=# insert into t1 select id, point(random()500, random()500) from generate_series(1,10000) t(id);
INSERT 0 10000
```
3、查询每个点,属于哪个面。
方法1,JOIN
```
postgres=# explain analyze select t1.,t2. from t1 join t2 on (t2.pos @> box(t1.pos, t1.pos));
QUERY PLAN
Nested Loop (cost=0.29..73322.20 rows=2510010 width=56) (actual time=0.094..1191.076 rows=10000 loops=1)
-> Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..116.00 rows=10000 width=20) (actual time=0.020..1.047 rows=10000 loops=1)
-> Index Scan using idx_t2 on t2 (cost=0.29..4.81 rows=251 width=36) (actual time=0.039..0.118 rows=1 loops=10000)
Index Cond: (pos @> box(t1.pos, t1.pos))
Planning time: 0.102 ms
Execution time: 1191.619 ms
(6 rows)
```
方法2,SUBQUERY
```
postgres=# explain analyze select t1.*, (select t2 from t2 where t2.pos @> box(t1.pos,t1.pos) limit 1) from t1;
QUERY PLAN
Seq Scan on t1 (cost=0.00..13706.74 rows=10000 width=52) (actual time=0.077..427.466 rows=10000 loops=1)
SubPlan 1
-> Limit (cost=0.29..1.36 rows=1 width=60) (actual time=0.042..0.042 rows=1 loops=10000)
-> Index Scan using idx_t2 on t2 (cost=0.29..269.88 rows=251 width=60) (actual time=0.042..0.042 rows=1 loops=10000)
Index Cond: (pos @> box(t1.pos, t1.pos))
Planning time: 0.080 ms
Execution time: 427.942 ms
(7 rows)
```
如果是1000笔订单,返回差不多40毫秒
``` postgres=# explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select t1.*, (select t2 from t2 where t2.pos @> box(t1.pos,t1.pos) limit 1) from t1 limit 1000; QUERY PLAN
Limit (cost=0.00..1370.67 rows=1000 width=52) (actual time=0.069..39.754 rows=1000 loops=1) Output: t1.id, t1.pos, ((SubPlan 1)) Buffers: shared hit=3002 -> Seq Scan on public.t1 (cost=0.00..13706.74 rows=10000 width=52) (actual time=0.069..39.658 rows=1000 loops=1) Output: t1.id, t1.pos, (SubPlan 1) Buffers: shared hit=3002 SubPlan 1 -> Limit (cost=0.29..1.36 rows=1 width=60) (actual time=0.039..0.039 rows=1 loops=1000) Output: t2. Buffers: shared hit=3000 -> Index Scan using idx_t2 on public.t2 (cost=0.29..269.88 rows=251 width=60) (actual time=0.039..0.039 rows=1 loops=1000) Output: t2. Index Cond: (t2.pos @> box(t1.pos, t1.pos)) Buffers: shared hit=3000 Planning time: 0.066 ms Execution time: 39.830 ms (16 rows) ```
因为@>暂时不支持hash join,因此subquery更优一些。
本文没有用到PostGIS空间数据库插件,而是使用了内置的平面几何类型,用于演示。
真实场景请使用PostGIS。
http://postgis.net/
例如
select t1.*, (select t2 from t2 where ST_Within(t1.geom, t2.geom) limit 1) from t1;
小结
点面判断在GIS信息崛起的今天,在越来越多的企业中成为了非常常见的需求,比如文中提到的。
PostgreSQL在空间数据库领域有非常丰富的应用,从科研、军工、商业到民用,无处不在。
结合空间索引,BRIN索引实现空间数据的高效率检索是很轻松的事情。
PostgreSQL 许愿链接
您的愿望将传达给PG kernel hacker、数据库厂商等, 帮助提高数据库产品质量和功能, 说不定下一个PG版本就有您提出的功能点. 针对非常好的提议,奖励限量版PG文化衫、纪念品、贴纸、PG热门书籍等,奖品丰富,快来许愿。开不开森.
9.9元购买3个月阿里云RDS PostgreSQL实例
PostgreSQL 解决方案集合
德哥 / digoal's github - 公益是一辈子的事.










