




BaseConversionGuide.pdf
5墨值下载
Base Conversion Guide
UCR · Math 135A
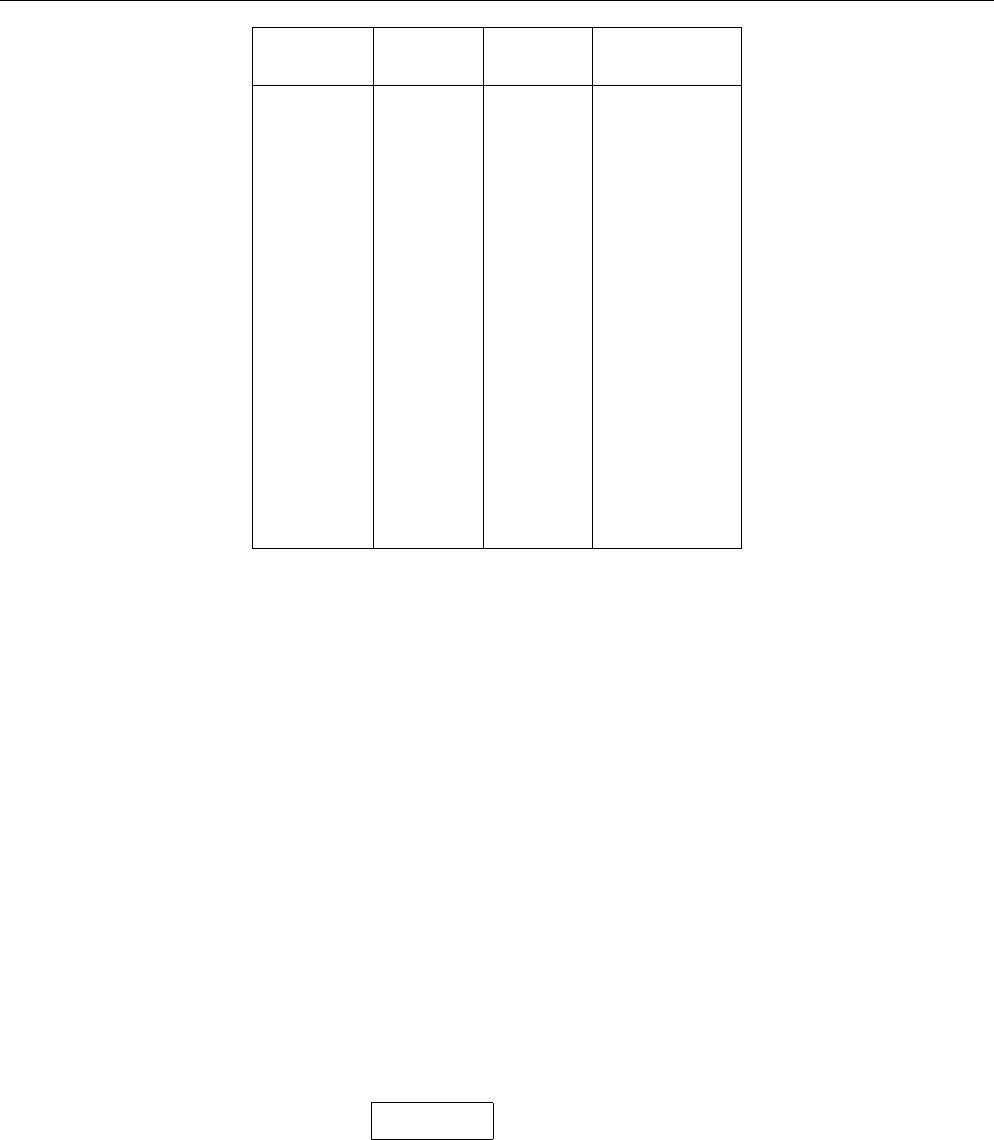
Decimal Binary Octal Hexidecimal
(Base 10) (Base 2) (Base 8) (Base 16)
0 0000 00 00
1 0001 01 01
2 0010 02 02
3 0011 03 03
4 0100 04 04
5 0101 05 05
6 0110 06 06
7 0111 07 07
8 1000 10 08
9 1001 11 09
10 1010 12 0A
11 1011 13 0B
12 1100 14 0C
13 1101 15 0D
14 1110 16 0E
15 1111 17 0F
1. Convert from base β to base 10.
Integer Part:
(a
n
a
n−1
· · · a
1
a
0
)
β
= a
n
∗ β
n
+ a
n−1
∗ β
n−1
+ ... + a
1
∗ β
1
+ a
0
∗ β
0
= (x)
10
Fraction Part:
(0.b
1
b
2
b
3
· · · )
β
= b
1
∗ β
−1
+ b
2
∗ β
−2
+ b
3
∗ β
−3
+ ...
= (x)
10
Example: Convert 21.112 in base 3 to base 10
(21.112)
3
= 2 ∗ 3
1
+ 1 ∗ 3
0
+ 1 ∗ 3
−1
+ 1 ∗ 3
−2
+ 2 ∗ 3
−3
= 2 ∗ 3 + 1 ∗ 1 + 1 ∗ .333 + 1 ∗ .111 + 2 ∗ .037
= 6 + 1 + .333 + .111 + .074
= (7.518...)
10
(1)
1

2. Convert from base 10 to base β.
Integer Part:
(a) Divide the number by β and record the remainder.
(b) Divide the resulting quotient by β and record the remainder.
(c) Repeat
(d) The number in base β is the remainders written in backwards order.
Fraction Part:
(a) Multiply the number by β and record the integer.
(b) Multiply the resulting number (ignoring the integer) by β and record the integer.
(c) Repeat
(d) The number in base β is the integers written in forwards order.
Example: Convert 15.4375 in decimal (base 10) to binary (base 2)
• First convert the integer part:
15 ÷ 2 = 7 R1
7 ÷ 2 = 3 R1
3 ÷ 2 = 1 R1
1 ÷ 2 = 0 R1
Hence (15)
10
= (1111)
2
.
• Second convert the fraction part:
0.4375 ∗ 2 = 0.8750
0.875 ∗ 2 = 1.750
0.75 ∗ 2 = 1.50
0.5 ∗ 2 = 1.0
Hence (0.4375)
10
= (0.0111)
2
• Final Answer: (15.4375)
10
= (1111.0111)
2
3. Convert from base α to base β.
• First convert from base α to base 10.
• Second convert from base 10 to base β.
2
4. Convert from decimal to single precision machine representation.
Steps:
(a) Identify the sign (length 1):
• 0 for +
• 1 for -
(b) Identify the mantissa (length 23):
• First, convert the decimal number (without the sign) to binary. It is recommended
to convert from base 10 to 8 to 2.
• Second, move the decimal forwards or backwards so that it is written in the the
form a.b
1
b
2
b
3
· · · × 2
n
where n is the number of spaces you moved the decimal (can
be positive or negative depending on the direction the decimal was moved).
• The mantissa is the number b
1
b
2
b
3
· · ·
• Add enough zeros to the mantissa so that it is 23 digits long.
(c) Identify the exponent (length 8):
• Solve c − 127 = n for c. You know n from calculation of the mantissa.
• Note that c is in base 10. Convert it to binary. Again it is recommended to convert
from base 10 to 8 to 2.
• If there is a leading 0, eliminate is so you have a number of 8 digits in length.
(d) Put it all together:
• Put the value for the sign in the first slot.
• Next write down the 8 digits of the number for the exponent step.
• Lastly write down the mantissa with the extra zeros so the number has a total of
32 digits.
(e) Convert to hexidecimal:
• Divide the 32 digit number into 8 numbers each of length 4.
• Convert each 4 digit number from binary to hexidecimal. This is your final answer.
Example: Convert -52.234375 to single precision machine representation.
(a) Identify the sign: The number is negative, which implies 1.
(b) Identify the mantissa:
• We will convert 52.234375 to binary:
First convert the integer part:
52 ÷ 8 = 6 R4
6 ÷ 8 = 0 R6
So (52)
10
= (64)
8
= (110 100)
2
Second convert the fraction part:
0.234375 ∗ 8 = 1.875000
0.875 ∗ 8 = 7.000
So (0.234375)
10
= (0.17)
8
= (0.001 111)
2
.
3
of 6
5墨值下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜
1
2
9-数据库人的进阶之路:从PG分区、SQL优化到拥抱AI未来(罗敏).pptx
3
1-PG版本兼容性案例(彭冲).pptx
4
2-TDSQL PG在复杂查询场景中的挑战与实践-opensource.pdf
5
6-PostgreSQL 哈希索引原理浅析(文一).pdf
6
8-基于PG向量和RAG技术的开源知识库问答系统MaxKB.pptx
7
3-AI时代的变革者-面向机器的接口语言(MOQL)_吕海波.pptx
8
4-IvorySQL V4:双解析器架构下的兼容性创新实践.pptx
9
7-拉起PG好伙伴DifySupaOdoo.pdf
10
《云原生安全攻防启示录》李帅臻.pdf


相关文档
评论