一个类只有一个实例化对象
全局可以使用
单例模式的基本实现:包含单例模式的实现,线程安全,以及生命周期等
单例模式的模板实现, 多模块调用单例存在的问题
单例模式的基本实现
私有的构造函数, 拷贝构造函数,以及
operator=
, 保证其不能够在类的外部进程对象构造,拷贝等操作。GetInstance
是一个公有的静态成员函数,用来构造这个类唯一的实例对象m_objConfig
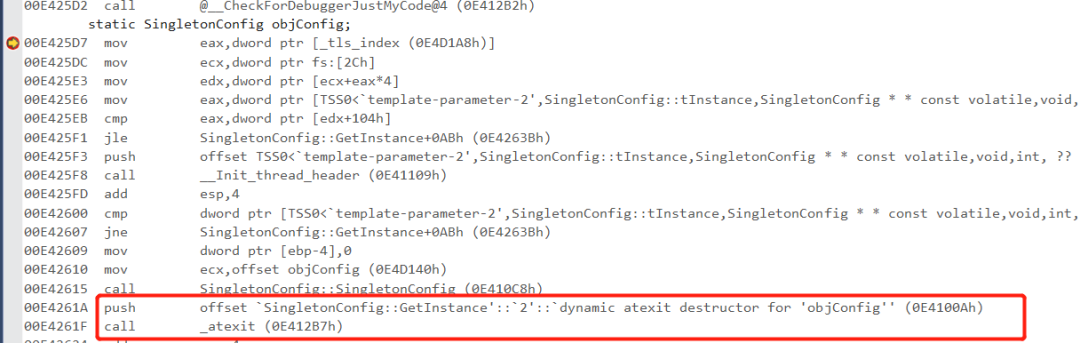
, 并且返回给使用者。
class SingletonConfig{public:static SingletonConfig * GetInstance(){if (m_objConfig = = nullptr)m_objConfig = new SingletonConfig;return m_objConfig;}private:SingletonConfig() { ; };SingletonConfig(const SingletonConfig&) { ; };SingletonConfig& operator= (const SingletonConfig&) { ; };private:static SingletonConfig *m_objConfig;};SingletonConfig* SingletonConfig::m_objConfig = nullptr;
单例模式生命周期
单例创建的时机
class SingletonConfig{public:static SingletonConfig * GetInstance(){return m_objConfig;}private:SingletonConfig() { ; };SingletonConfig(const SingletonConfig&) { ; };SingletonConfig& operator= (const SingletonConfig&) { ; };private:static SingletonConfig *m_objConfig;};SingletonConfig* SingletonConfig::m_objConfig = new SingletonConfig;
单例释放的时机
class SingletonConfig{public:static SingletonConfig * GetInstance(){static SingletonConfig objConfig;return &objConfig;}virtual ~SingletonConfig(){std::cout << "~SingletonConfig()" << std::endl;}private:SingletonConfig() { ; };SingletonConfig(const SingletonConfig&) { ; };SingletonConfig& operator= (const SingletonConfig&) { ; };};
class SingletonConfig{public:static SingletonConfig * GetInstance(){if (m_objConfig == nullptr)m_objConfig = new SingletonConfig;return m_objConfig;}static void ReleaseInstance(){if (m_objConfig){delete m_objConfig;m_objConfig = nullptr;}}virtual ~SingletonConfig(){std::cout << "~SingletonConfig()" << std::endl;}private:SingletonConfig() { ; };SingletonConfig(const SingletonConfig&) { ; };SingletonConfig& operator= (const SingletonConfig&) { ; };private:static SingletonConfig* m_objConfig;};SingletonConfig* SingletonConfig::m_objConfig = nullptr;
线程安全
static SingletonConfig * GetInstance(){static SingletonConfig objConfig;return &objConfig;}
static SingletonConfig * GetInstance(){if (m_objConfig == nullptr)m_objConfig = new SingletonConfig;return m_objConfig;}
使用
std::lock_guard
去多线程保证互斥双重的
m_objConfig == nullptr
检查,第一次是为了效率,当单例对象已经在的时候,就不需要互斥锁了;第二次是进入锁范围之后,要查看下,是否有其他线程已经创建了单例对象,如果还没有创建才进行创建。
class SingletonConfig{public:static SingletonConfig * GetInstance(){if (m_objConfig == nullptr){std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(m_mutex);if (m_objConfig == nullptr){m_objConfig = new SingletonConfig;}}return m_objConfig;}static void ReleaseInstance(){if (m_objConfig){delete m_objConfig;m_objConfig = nullptr;}}virtual ~SingletonConfig(){std::cout << "~SingletonConfig()" << std::endl;}private:SingletonConfig() { ; };SingletonConfig(const SingletonConfig&) { ; };SingletonConfig& operator= (const SingletonConfig&) { ; };private:static SingletonConfig* m_objConfig;static std::mutex m_mutex;};SingletonConfig* SingletonConfig::m_objConfig = nullptr;std::mutex SingletonConfig::m_mutex;
单例模式的模板实现以及可能的问题
template<typename T>class CommonSingleton{public:static T* GetInstance(){if (m_objSingle == nullptr){std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(m_mutex);if (m_objSingle == nullptr){m_objSingle = new T;}}return m_objSingle;}static void ReleaseInstance(){if (m_objSingle){delete m_objSingle;m_objSingle = nullptr;}}private:CommonSingleton() { ; };CommonSingleton(const CommonSingleton&) { ; };CommonSingleton& operator= (const CommonSingleton&) { ; };private:static T* m_objSingle;static std::mutex m_mutex;};template<typename T>T* CommonSingleton<T>::m_objSingle = nullptr;template<typename T>std::mutex CommonSingleton<T>::m_mutex;
CommonSingleton<TestClass>::GetInstance();
模板参数接受的类,可以是这种:默认暴露给用户,可以构造,拷贝,赋值的类,这样便可以重新创造多个对象。这种方式缺乏了本人所理解的
防御性
编程的思路。当使用模板实例化的时候,同一种模板参数的类,在多个不同的模块中其实都会有自己的实例化对象。比如有A和B两个模块,并且均调用了
CommonSingleton<TestClass>::GetInstance();
, 其实在A和B中存在不同的TestClass
对象,这样也违背了一个程序一个实例化对象的初衷。当然只有一个工程不影响。对于非模板的实现,一般将单例实现的类从模块导出,将实现放在.cpp
文件中,那么这种多个工程对同一种单例的类只会有一个实例化对象。个人觉得这一点比较重要,需要读者多多体会。
总结
参考
<<C++设计新思维>>
中的Singletons实作技术这一章节<<深入应用C++11代码优化及工程级应用>>
的改进单例模式这一章节
文章转载自一个程序员的修炼之路,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。